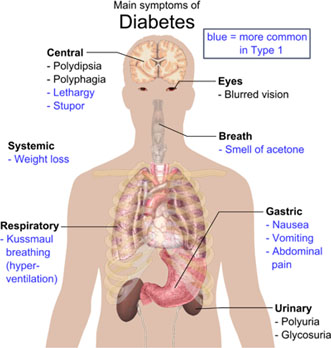
Central
Polydipsia is a condition in which the patient displays excessive thirst. This symptom is most commonly observed in diabetics and may be a result of a poorly controlled or undiagnosed diabetic condition.
Polyphagia is the medical term used to describe an increase in appetite or excessive hunger. It is one of the main signs of diabetes. A person who has polyphagia must be examined by a physician to confirm that it is a symptom of diabetes
Lethargy is the state of being drowsy and dull, listless and unenergetic. A diabetic fails to utilize the sugar in his blood properly making him feel lethargic.
A Stupor is a condition of greatly dulled or completely suspended sense or sensibility. In diabetes, prolonged periods of elevated blood sugar levels may lead to damage to brain cells causing stupor like conditions.
Systemic
Unexplained Weight loss leading to a rapid decrease in body weight, may be a warning sign of diabetes. In people with diabetes, insufficient insulin prevents the body from utilizing glucose from the blood for energy. When this occurs, the body starts burning fat and muscle to convert into energy, causing weight loss.
Respiratory
Kussmaul breathing/hyperventilation is deep and labored breathing with increase in frequency. It is observed in people with diabetic ketoacidosis leading to coma.
Eyes
Blurred Vision is one of the common signs of, which refers to the loss of sharpness of vision and the inability to see fine details. In diabetes, prolonged increase in blood sugar levels can affect your ability to see by causing the eye-lens to swell, which may result in blurred eyesight.
Breath
Smell of Acetone
One common sign that a person’s diabetes and acetone levels are out of control is the presence of acetone breath. Acetone begins to accumulate in the body when a person with diabetes skips meals, does not take medications on time, or has not administered enough insulin.
Gastric
Nausea
About 5%–12% of diabetes patients develop a digestive complication called gastroparesis1-2, in which movement of food from stomach to intestines is slower than normal. Gastroparesis develops when high blood glucose levels (as in diabetes) cause chemical changes that damage the vagus nerve.
Vomiting
People with diabetes develop vomiting when their blood sugars become abnormally high or low (hyperglycemia or hypoglycemia) because the sugar and insulin balance is disturbed.
Abdominal Pain
Diabetic individuals with poor control of their blood sugar levels are more prone to developing Candida yeast infections in their gastrointestinal tract than people with controlled blood glucose levels. This may in turn lead to stomach pain.
Urinary
Polyuria is a condition in which the body urinates more than usual and passes excessive or abnormally large amounts of urine each time you urinate. Polyuria is most commonly caused by diabetes. In diabetes, the level of sugar in the blood is higher than normal. Some of this excess glucose from the blood ends up in the urine where it draws more water. This results in unusually large volumes of urine.
Glycosuria
The most common reason for glycosuria is diabetes mellitus. Diabetes mellitus causes excessive glucose in the blood that leads to the leakage of glucose into the urine.



